Imaging
|
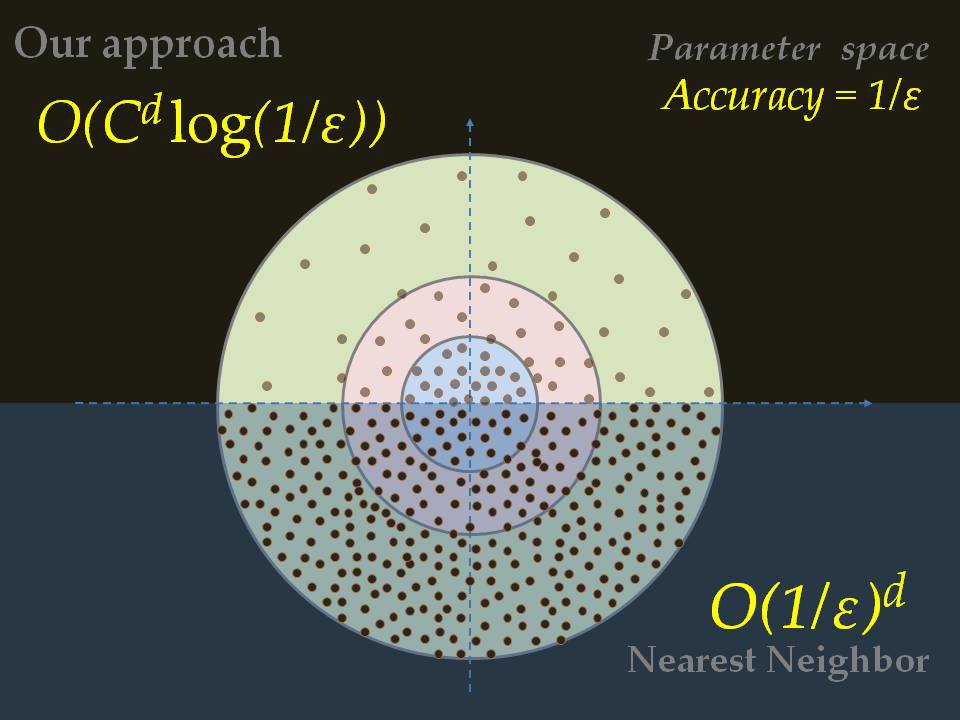
We present a simple but powerful self-supervised domain adaptation of person appearance descriptor framework using monocular motion tracking, mutual exclusive constraints, and multi-view geometry without manual annotations. Our discriminative appearance descriptor allows a reliable association via simple clustering. This advantage enables a first-of-a-kind accurate and consistent markerless motion tracking of multiple people participating in a complex group activity from mobile cameras in the wild, with further application to multi-angle video for intuitive tracking visualization.
|
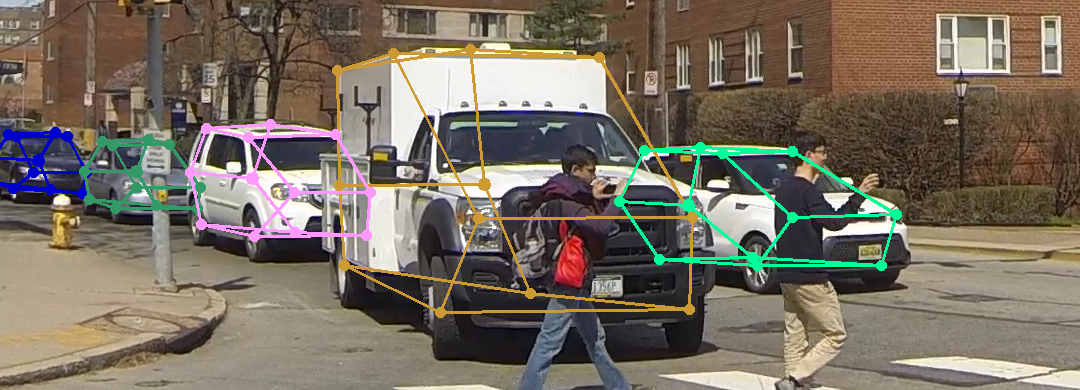
We present Occlusion-Net a framework to predict 2D and 3D locations of occluded keypoints for objects, in a largely self-supervised manner. A graph encoder network then explicitly classifies invisible edges and a graph decoder network corrects the occluded keypoint locations from the initial detector. The 2D keypoints are then passed into a 3D graph network that estimates the 3D shape and camera pose using the selfsupervised reprojection loss.
|

We present the first comprehensive dataset and approach for powder recognition using multi-spectral imaging. By using Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) multi-spectral imaging together with visible light (RGB) and Near Infrared (NIR) and incorporating band selection and image synthesis, we conduct fine-grained recognition of 100 powders on complex backgrounds and achieve reasonable accuracy.
|
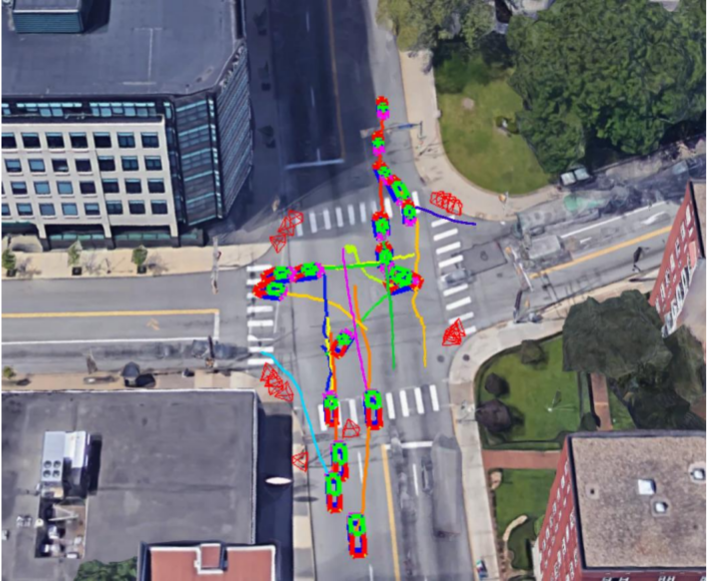
Unstructured local feature can be reliably tracked within each view but is hard to match across multiple views. Structured semantic feature can be easily matched across views but is still not precise enough for triangulation based reconstruction. We develop a framework to fuse both the single-view unstructured feature tracks and multiview structured part locations to significantly improve the detection, localization and reconstruction of moving vehicles. We demonstrate our method at a busy traffic intersection by reconstructing over 40 vehicles passing within a 3-minute window.
|

We propose an image formation model that explicitly describes the spatially
varying optical blur and mutual occlusions for structures located at different
depths. Based on the model, we derive an efficient MCMC inference algorithm
that enables direct and analytical computations of the iterative update for the
model/images without re-rendering images in the sampling process. Then, the
depths of the thin structures are recovered using gradient descent with the
differential terms computed using the image formation model.
We apply the proposed method to scenes at both macro and micro scales.
|
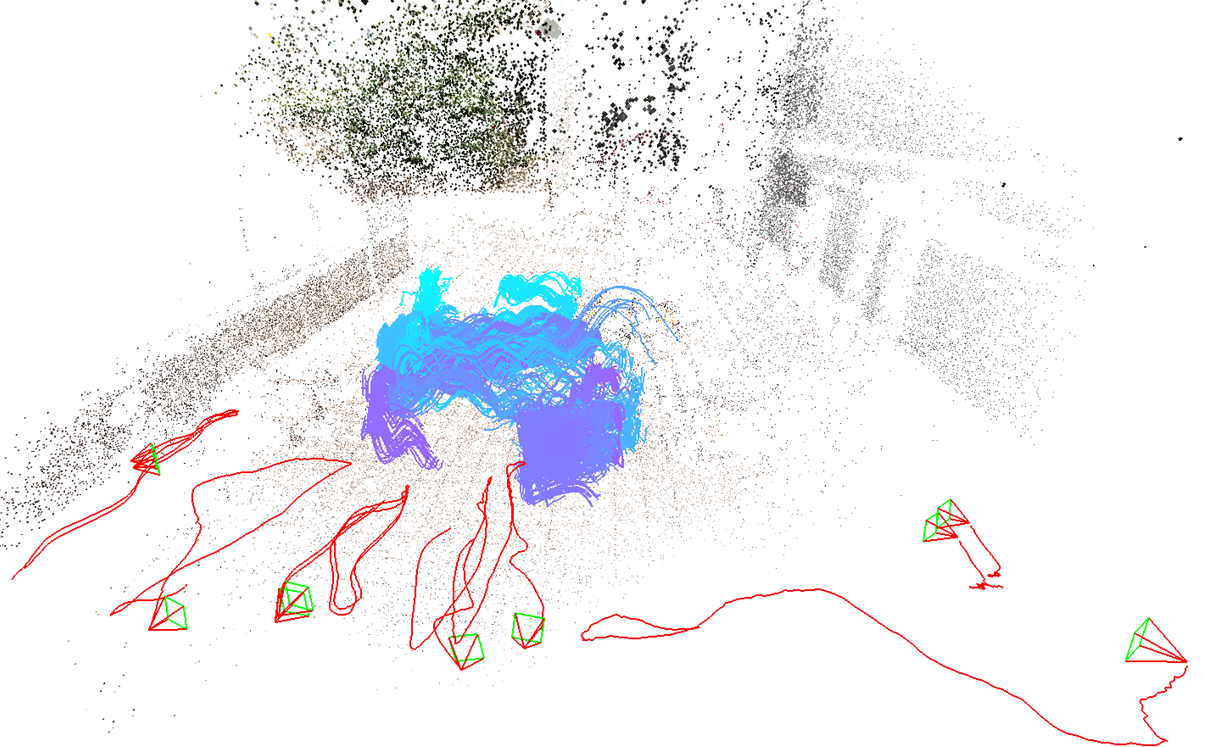
We develop a method to estimate 3D trajectory of dynamic objects
from multiple spatially uncalibrated and temporally unsynchronized cameras.
Our estimated trajectories are not only more accurate and but also have much longer and
higher temporal resolution than previous arts.
|

In this project we develop a light efficient method of performing transport probing operations like epipolar
imaging. Our method enables structured light imaging to be performed effectively under bright ambient light conditions with a low power
projector source.
|
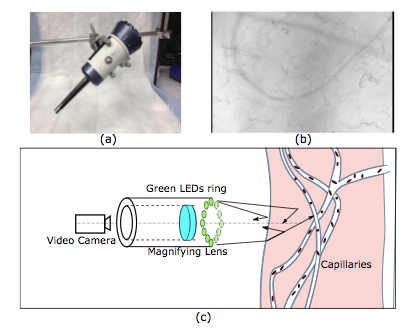
In this project, we develop real time tools to capture and analyze blood circulation in micro vessels that
is important for critical care applications. The tools provide highly detailed blood flow statistics for bedside and surgical care.
|

This project explores an inexpensive method to directly estimate Turblence Strength field by using
only passive multiview observations of a background.
|

The project aims to model the optical turbulence through hot air and
exploits the model to remove turbulence effects from images as well as recover depth cues in the scene.
|

The image of a deformed document is
rectified by tracing the text and recovering the 3D
deformation.
|
The deformation field between a distorted image and the corresponding
template is estimated. Global optimality criteria for the estimation are derived.
|
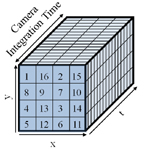
We wish to build video cameras whose spatial and temporal resolutions can
be adjusted post-capture depending on the motion in the scene.
|

Multiple coded exposure cameras are used to obtain temporal super-resolution.
|

We present a practical approach to SFS using a novel technique called coplanar shadowgram imaging, that allows us to use dozens to even hundreds of views for visual hull reconstruction.
|

We generalize dual photography for all types of light-sources using opaque, occluding masks.
|
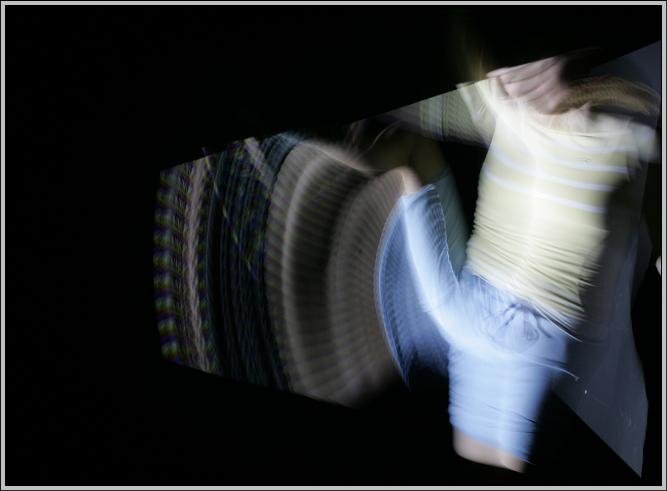

We process photographs taken under DLP lighting to either summarize a dynamic scene or illustrate its motion.
|

We estimate the shape of the water surface and recover the underwater scene without using any calibration patterns, multiple viewpoints or active illumination.
|
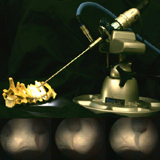
We present a complete calibration of oblique endoscopes.
|

This page describes a new technology developed at Columbia's Computer Vision Laboratory that can be used to enhance the dynamic range (range of measurable brightness values) of virtually any imaging system.
|