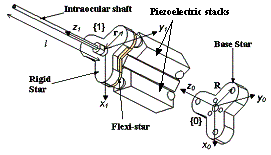
Micron 1 Manipulator
Fig. 1a & b depicts the
3 DOF parallel robotic manipulator that deflects the tip of the
instrument. We have 6 DOF sensing but only 3 DOF manipulations because the
workspace is small enough that changes in shaft orientation due to the
micromanipulator deflection are negligible with regard to the performance
of practical surgical tasks. Piezoelectric actuators
were chosen for their high bandwidth, fast response time, high actuation
force and miniature size. A range of motion of 100 Ám or greater has been
achieved in each of the three coordinate directions by stacking 7
piezoelectric elements (TS18-H5-202, Piezo Systems, Inc., Cambridge, Ma.)
to form each actuator. The stainless steel tool
shaft is affixed to the center of a three-pointed rigid star. Beneath the
rigid star is a thin flexible star made of ABS 780 thermoplastic. The tip
of each leg of the rigid star is pinned to the tip of the corresponding
leg of the flexible star. At its center the flexible star is bolted to the
triangular center column, constraining it against axial rotation and
against translation in the two coordinates transverse to the long axis of
the instrument. The maximum attainable tip displacement and velocity of the manipulator are summarized in Table I.
Table I
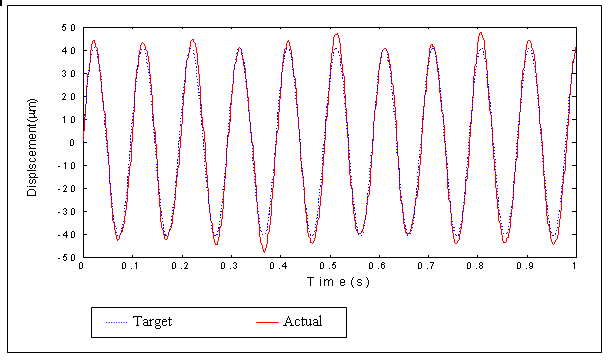
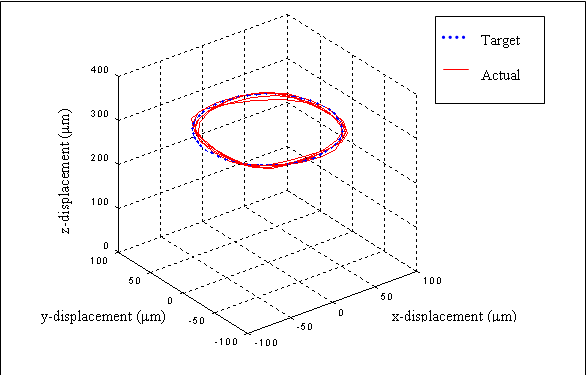
Experimental results show
that the prototype is able to track 1-D and 3-D trajectories with rms
error of 2.5 Ám and 11.2 Ám respectively in open-loop control.
Publications: 1.
An Active Hand-held
Instrument for Enhanced Microsurgical Accuracy
Intervention, Springer, October, 2000,
pp. 878-886. [Abstract] |