Cascade-correlation
neural networks with extended Kalman filtering
In order to cancel the
largely unknown non-tremulous erroneous motion, we have begun
experiments with a constructive neural network algorithm, the
cascade-correlation learning architecture, as modified by Nechyba and Xu
for modeling of human control behavior. Preliminary tests of this
technique in simulation with recorded instrument motion data have
yielded an average rms error reduction of 40%. The signal used in place
of voluntary motion in this simulation was an artificial signal
consisting of white noise bandlimited to 1 Hz. Fig. 2 shows the results
of a typical experiment.
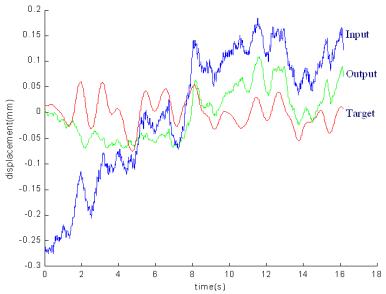
Fig. 2. Typical canceling results for non-tremulous error using the cascade-correlation learning architecture. The target line shows the simulated voluntary motion (white noise bandlimited to 1 Hz). The network input for the test is obtained by adding recorded hand motion error to the voluntary motion. The filtered output of the neural network is visibly closer to the target (voluntary) signal than is the original net input. This figure presents testing data only; no network training
is taking place in the trial shown.
Publications: 1.
Neural network
methods for error canceling in human-machine manipulation |