The KL Procedure
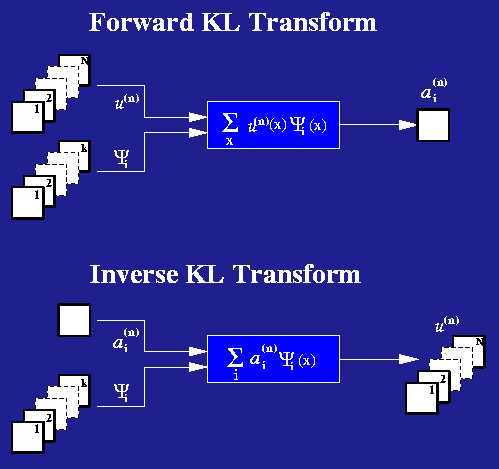

The empirical eigenfunctions of the K-L procedure can be used to decompose the dataset from which they are calculated. In the diagram above, the forward transform and inverse transform are shown.
The forward transform consists of correlating each eigenfunction, or basis function, with each frame of data. The result is a set of coefficients {a} which are indexed by the frame and the basis function used in the correlation. The original frame of Nx by Ny is decomposed into N scalar coefficients, where N is the number of basis functions. This represents a very large compression of data.
In the inverse transform, the coefficients {a} are used as weights for the basis functions in a weighted sum. The result of the weighted sum is the original frame of data.
This procedure is the same as it would be for a Fourier analysis, with the coefficients calculated by an inner product of basis functions and data, and the reconstruction of the data by a weighted sum using the coefficients from the forward transform.
Eigenfunction Analysis of Coherent Structures on the Solar Surface
Authoring NASA Official:Dr. Milton Halem, Chief, Earth
and Space Data Computing Division
Contact:Marilyn Mack/Code 930
marilyn.j.mack.1@gsfc.nasa.gov