

This implies that there is no contribution of the jth eigenfunction in the ith eigenfunction when i is not equal to j. In other words, if we find a certain amount of an eigenfunction present in a snapshot of the system that doesn't say anything about any other eigenfunction.
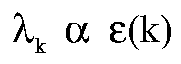
This comes directly from the fact that the eigenfunctions diagonalize the K matrix to form a diagonal matrix of eigenvalues.

using the first M eigenfunctions, for any M. This implies that no other orthonormal basis set can do a better job of representing the original data than the KL empirical basis functions. This has several implications in different applications. For instance, in Information Theory, it means that the information entropy is minimized with the KL transform. In Image Processing, it means that the KL transform is the optimal data compression scheme for a set of images. For our problem, it means that given a set of snapshots of a system, the KL basis functions are the primary modes of the system.
Eigenfunction Analysis of Coherent Structures on the Solar Surface
Authoring NASA Official:Dr. Milton Halem, Chief, Earth
and Space Data Computing Division
Contact:Marilyn Mack/Code 930
marilyn.j.mack.1@gsfc.nasa.gov