



Next: Benefit of cycle stealing:
Up: Mean response time
Previous: Mean response time
Contents
Benefits of cycle stealing: wide range 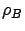
Figure 6.4:
The mean response time for beneficiary jobs and donor jobs as a function of 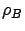 under cycle stealing
and dedicated servers. In all figures
under cycle stealing
and dedicated servers. In all figures 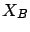 and
and  are
exponential with mean 1; switching times (
are
exponential with mean 1; switching times (
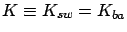 ) are exponential with mean 0 or
1 as labeled.
) are exponential with mean 0 or
1 as labeled.
Mean response time: low-to-medium load: 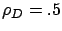
|
beneficiary
response time
|
(a)
![$\mbox{{\bf\sf E}}\left[ K \right]=0$](img1459.png) |
(b)
![$\mbox{{\bf\sf E}}\left[ K \right]=1$](img1461.png) |
Mean response time: medium-to-high load: 
|
beneficiary
response time
|
(c)
![$\mbox{{\bf\sf E}}\left[ K \right]=0$](img1459.png) |
(d)
![$\mbox{{\bf\sf E}}\left[ K \right]=1$](img1461.png) |
|
Cycle stealing is always a win when 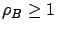 , but does not pay when
, but does not pay when
 .
.
Figure 6.4 shows the mean
response time for beneficiary jobs (rows 1 and 3) and donor jobs (rows 2 and 4)
as a function of 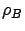 , where
, where 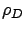 is low-to-medium
(
is low-to-medium
(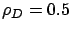 ; top half) and medium-to-high (
; top half) and medium-to-high ( ;
bottom half). When
;
bottom half). When 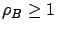 (and
(and  ), cycle
stealing can provide infinite gain to beneficiary jobs over dedicated
servers, with comparatively little pain for the donor jobs. This is
because the stability region for the beneficiary jobs under cycle
stealing is much greater than under dedicated servers. While factors
such as increased switching times and increased
), cycle
stealing can provide infinite gain to beneficiary jobs over dedicated
servers, with comparatively little pain for the donor jobs. This is
because the stability region for the beneficiary jobs under cycle
stealing is much greater than under dedicated servers. While factors
such as increased switching times and increased 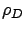 do increase
the mean response time of the beneficiary jobs, the gain is still
infinite, and these factors are less important. We also see that the
mean response time of donor jobs is bounded by the mean response time
for an M/GI/1 queue with setup time
do increase
the mean response time of the beneficiary jobs, the gain is still
infinite, and these factors are less important. We also see that the
mean response time of donor jobs is bounded by the mean response time
for an M/GI/1 queue with setup time 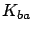 . When
. When
 , there is so little gain to the beneficiary jobs that cycle
stealing with non-zero switching overhead does not pay. We therefore
primarily focus the rest of the results section on the remaining case:
, there is so little gain to the beneficiary jobs that cycle
stealing with non-zero switching overhead does not pay. We therefore
primarily focus the rest of the results section on the remaining case:
 .
.




Next: Benefit of cycle stealing:
Up: Mean response time
Previous: Mean response time
Contents
Takayuki Osogami
2005-07-19
, but does not pay when
.
![]() , where
, where ![]() is low-to-medium
(
is low-to-medium
(![]() ; top half) and medium-to-high (
; top half) and medium-to-high (![]() ;
bottom half). When
;
bottom half). When ![]() (and
(and ![]() ), cycle
stealing can provide infinite gain to beneficiary jobs over dedicated
servers, with comparatively little pain for the donor jobs. This is
because the stability region for the beneficiary jobs under cycle
stealing is much greater than under dedicated servers. While factors
such as increased switching times and increased
), cycle
stealing can provide infinite gain to beneficiary jobs over dedicated
servers, with comparatively little pain for the donor jobs. This is
because the stability region for the beneficiary jobs under cycle
stealing is much greater than under dedicated servers. While factors
such as increased switching times and increased ![]() do increase
the mean response time of the beneficiary jobs, the gain is still
infinite, and these factors are less important. We also see that the
mean response time of donor jobs is bounded by the mean response time
for an M/GI/1 queue with setup time
do increase
the mean response time of the beneficiary jobs, the gain is still
infinite, and these factors are less important. We also see that the
mean response time of donor jobs is bounded by the mean response time
for an M/GI/1 queue with setup time ![]() . When
. When
![]() , there is so little gain to the beneficiary jobs that cycle
stealing with non-zero switching overhead does not pay. We therefore
primarily focus the rest of the results section on the remaining case:
, there is so little gain to the beneficiary jobs that cycle
stealing with non-zero switching overhead does not pay. We therefore
primarily focus the rest of the results section on the remaining case:
![]() .
.