Shape Deposition Manufacturing
Sara Lechleitner
Michelle Pitkethley
Matt Dennerline
How is design information transmitted to the manufacturing process?
What are the size and shape limitations on the parts?
How quickly can parts be manufactured?
|
SDM is a solid freeform fabrication process which means it is built from start to finish rather than by removing excess materials from a given object. It does this by layering support material and the desired finished material. These graphics show the blue support material and the yellow final products.
|
|
How is design information transmitted to the manufacturing process?
Part information is drawn in a 3D CAD model. Then, the part is broken into thin two dimensional layers that are sent to the SDM machine. This tells the machine where to place the support or part material and when a new layer is necessary.
SDM can be used with any castable material especially plastics, metals, resins, polymers and ceramics. When using ceramics, a mold is made of the support material and then the desired material is cast inside of it.
 |
|
What are the size and shape limitations on the parts?
Almost any shape can be manufactured because SDM allows complicated convex and asymmetrical parts to be supported during the fabrication process. The size of the part is limited only by the size of the machine.
Since this an experimental process, the cost of parts changes constantly based on size, shape, material, availability, and advances in technology.
How quickly can parts be manufactured?
Because of the dramatic differences in the way individual parts are made, manufacturing time can vary greatly. The number of layers needed, the amount of support material, the number of embedded objects, and the availability of the machine are all contributing factors.
|
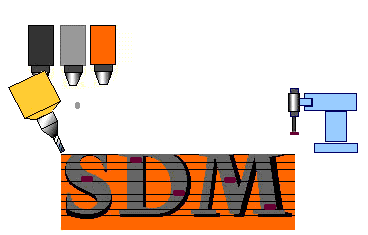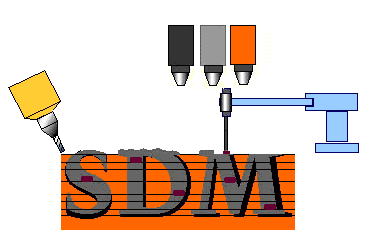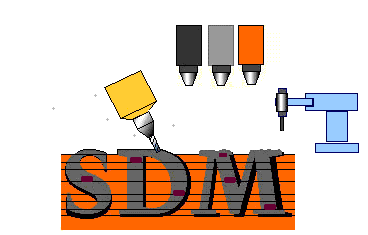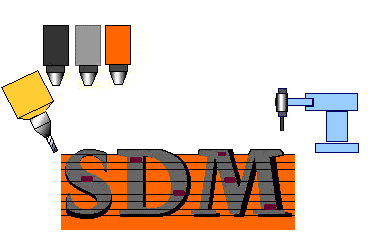
An advantage of SDM is the
ability to embed objects into the part as it is being manufactured.
This could include electronic equipment that needs precise placement in
the object. It is also possible to use different materials within
the same part. This process is illustrated in the figure to the
right. |

|
Relatively expensive compared to other rapid prototyping processes.
Also, the process is relatively time consuming.
The machine is not widely available.
All figures are courtesy of the Robotics
Institute at Carnegie Mellon University.
Additional information was found at the Rapid Prototyping Laboratory of Stanford University