- Wish to augment the capabilities of a human
- Wish to avoid having a human do dangerous or undesireable work
- Wish to benefit human life. (Biomedical applications)
- They are just plain fun.
- Navigation
- Mapping
- Coverage

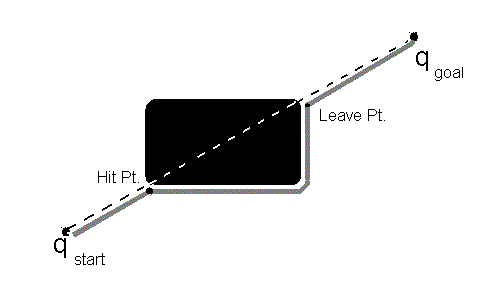
- Head toward the goal in a straight line.
- If you hit an obstacle, circumvent it until you reach the line connecting the start and goal, called the mline.
- If the leave point is closer to the hit point continue toward the goal in a straight line
- Else, continue around the obstacle
- If you return to the same hit point without defining a leave point, then you have gone completely around the obstacle and the goal is not reachable (return failure.)
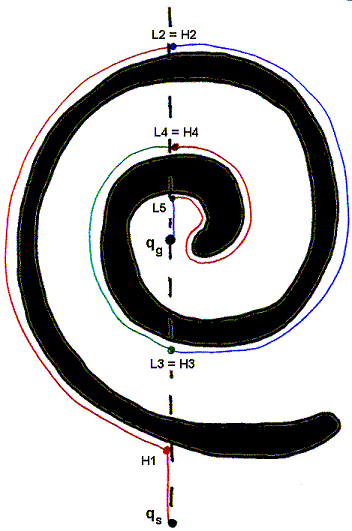
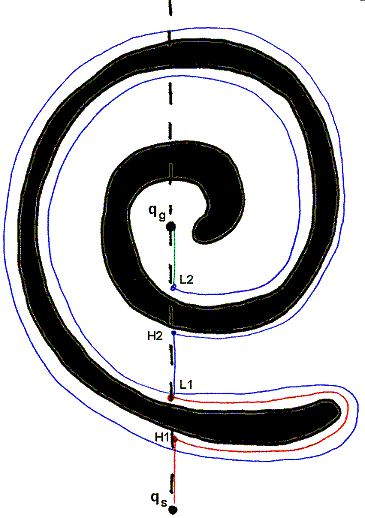
BUG2 with LEFT direction BUG2 with RIGHT direction
- Charge-analogy

- Distance Function (L1 and L2)


D(x) = min di(x) - Attractive/Repulsive Potential Functions
- Attractive: Distance to goal
- Repulsive: Distance to obstacles