Page 5: Acquire Engine
Architecture
Contributed by Lisa Anthony
Revised by Xuan Thuy Tran
[Go back to Page 4: User-Interaction Interface Subsystem | Go on to Page 6: Communications Superstructure ]
1 OverviewThe Acquire Engine is used by the Agents to plan and act in the world during game play. The Engine contains the information about the current state of the world, and the rules which govern Agent (i.e., player) manipulation of that state.
Referee Engine:Accessible by all Agents, this instance of the Engine controls the actual game progress, storing the concrete state of the world and guiding Agent game play by taking moves from the Agent whose turn it currently is and updating the state of the world. It is also responsible for telling the Agent what the world actually looks like when it is that Agent's turn (i.e., to reflect changes in the world caused by other Agent turns).
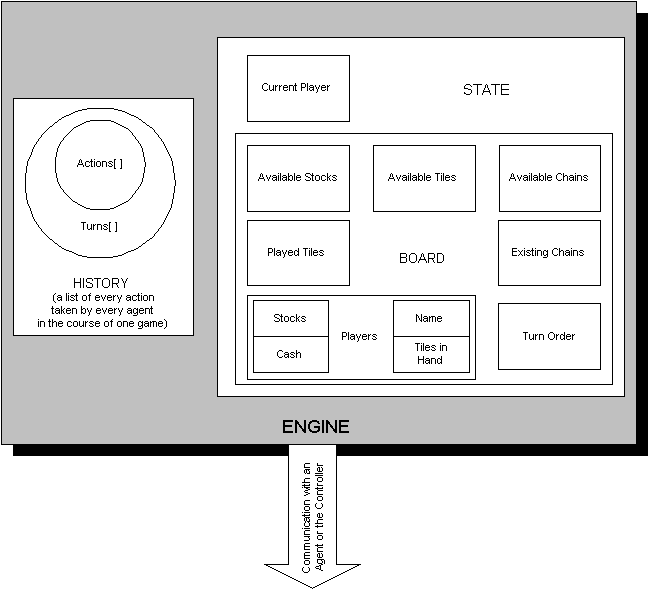
A diagram of the Engine appears below:
Figure 1-1: An overview of the Acquire Engine
2 The Engine ArchitectureAcquire's rules are built into the Acquire Engine. The Referee Engine enforces them by performing validity checks on moves the current Agent submits. The Referee Engine is responsible for controlling the flow of the game and keeping track of state and so on. When the game is in an endable state, the Referee Engine asks the current player Agent if it wants to end the game. If yes, the end-game tallying of standings occurs; if no, the game continues and play proceeds to the next player. For the benefit of readers unfamiliar with the game, the rules appear in the Acquire Rules section of this document.
4 Acquire Engine Class Structure
Engine: The main superclass for the Acquire Engine
architecture.
|
Fields: control :: the control of game progress board :: the virtual representation of the physical board and important attributes thereof history :: a list of all moves made/Actions taken during the course of the game by each Agent Methods: getHistory( ) :: returns the entire History (to the Controller who will use this method to get the History and dump it to a file) declareWinner( ) :: determines and announces the winner of the game |
State: The object used to encapsulate a state and pass it between objects (i.e., Agents and Heuristics).
|
Fields: board :: the current configuration of the board currentPlayer :: the Agent player who is making a move numberOfPlayers :: the number of Agent players in this game playerList[ ] :: a list of the Agent Players Methods: getPlayerList( ) :: returns the list of Agent names and/or numbers and their associated Heuristics, for this session getCurrentPlayer( ) :: returns the number of the Agent player currently making a move (other methods are also available, via the interface of the Board class) |
Board: The virtual representation of the physical board and
important attributes thereof.
|
Fields: availTiles[ ] :: a list of all tiles that have not yet been chosen availStocks[ ] :: a list of the amounts of stock shares not yet sold for each hotel chain availChains[ ] :: a list of the hotel chains which have not yet been defined on the board playedTiles[ ] :: a list of all tiles which have been placed on the board existingChains[ ] :: a list of all hotel chains which have been defined in this game and their sizes Methods: getNextPlayer( ) :: returns the number of the Agent whose turn is next (after the current turn finishes) getPlayerHeuristic (int player) :: returns the name of the Heuristic by which Agent "player" is playing during this session getAvailTiles( ) :: returns the pool of remaining available tiles getAvailStocks(string chain) :: returns the number of stock shares still available for the hotel chain "chain" getAvailChains( ) :: returns the list of chains which have not yet been defined getPlayedTiles( ) :: returns the list of all tiles currently on the board getExistingChains( ) :: returns the list of all existing chains getTilesInChain (string chain) :: returns the list of tiles in the hotel chain "chain" getChainSize (string chain) :: returns the size of the hotel chain "chain" |
History: A list of all Actions performed by each Agent during
the course of the game.
|
Fields: moves[ ] :: the list of all moves (Actions) made by every Agent during this game Methods: getMove (int i) :: returns the "i"th move in the history (from the first move) getPlayerMoves (int player) :: returns all moves made during this game by Agent "player" |
Player: The virtual representation of an Acquire player and
its assets.
|
Fields: name :: the name or IP location of the Acquire Agent representing this player during the session cash :: the amount of cash assets this Player possesses stocks[ ] :: a list of the stocks owned by this Player, and quantities thereof tilesInHand[ ] :: a list of the tiles currently in this Player's hand Methods: getName( ) :: returns the name or IP location of this Player's representative Acquire Agent get/setCash( ) :: returns or sets the amount of cash this Player currently possesses get/setNumStocks (string chain) :: returns or sets the quantity of stocks owned by this Player in hotel chain "chain" addStocks (string chain, int quantity) :: adds "quantity" of stocks in hotel chain "chain" to this Player's stocks removeStocks (string chain, int quantity) :: removes "quantity" of stocks in hotel chain "chain" from this Player's stocks getTileFromHand (string tile) :: removes "tile" from this Player's hand addTileToHand (string tile) :: adds "tile" to this Player's hand |
Turn: A representation of a complete Agent turn, which consists of several Actions (usually "place-tile", "buy-stock", and "draw-tile", but sometimes others). The Agent who made this Turn is also accessible via the Turn object.
|
Fields: |
Action: The representation of the operations an Agent might perform as its move (i.e., "place tile A6" would translate to verb="place-tile" and args[0]="A6"; "buy 4 stocks in Continental" would translate to verb="buy-stocks" and args[0]="4" and args[1]="Continental", for example)
|
Fields: verb :: the operation the Agent player wishes to perform (in the context of making a move) args :: the thing(s) being acted upon; the object(s) of the specific action Methods: getCurrentPlayer( ) :: returns the verb getArgs( ) :: returns the argument(s) |
The list of Actions which can take place in Acquire are:
place-tile Xbuy-stock qty Xsell-stock qty Xtrade-stock qty X Ydraw-tilehold-stock qty XThe following diagram depicts how all of the above objects interact with one another in the Acquire Engine to meet the description that was given in the overview.
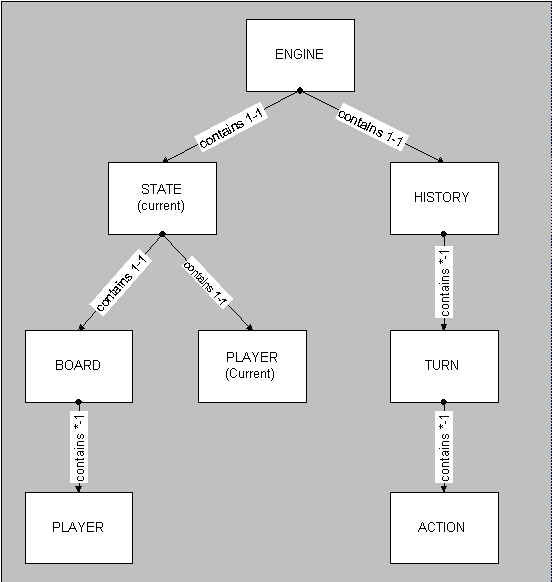
Figure 5-1: The Acquire Engine UML Diagram.
[Go back to
Page 4: User-Interaction Interface Subsystem | Go
on to Page 6: Communications Superstructure ]