The goal of this testing is to decide whether our project will purchase a Crossbow vertical gyro for use on our tractor. We have used KVH gyros in the past with good results. In these tests, we will compare the performance of the two devices to see whether the Crossbow will meet our needs.
The specific devices we are comparing are:
Crossbow VG600CA-200 Vertical Gyro
KVH ECore 2000 Single Axis Gyro
| Quantity | KVH ECore 2000 | Crossbow VG600CA-200 |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | 100 Hz | 100 Hz |
| Update Rate | 100 Hz | >80Hz |
| Max Angular Rate | 100 deg/sec | 200 deg/sec |
| Resolution | 0.003 deg/sec | 0.01 deg/sec |
| Scale Factor Accuracy | 2 % | 1 % |
| Non-Linearity | 0.5 % | 0.3 % |
| Random Walk | 0.3 deg/hr | 1.25 deg/hr |
| Bias | 0.08 deg/sec | 0.03 deg/sec |
An interface to the two sensors was developed under QNX6. As shown below, the interface allows zeroing the devices, sets the erection rate of the Crossbow vertical gyro, controls logging to files, and displays the current pitch/roll reported by the Crossbow as well as a zoomable time history of the angular rates for the two devices.

A metal cage was constructed around the Crossbow vertical gyro such that the KVH gyro could be attached to any side, thereby allowing a comparison of any of the three axes.
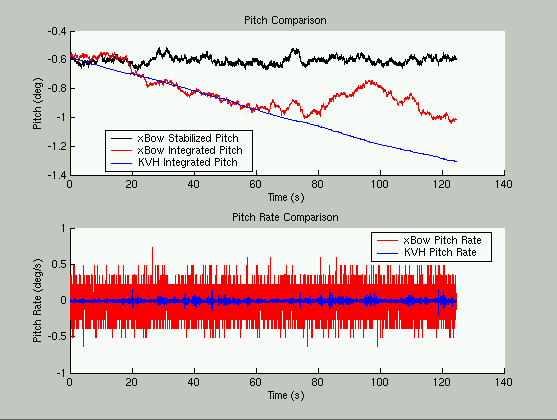
Two tests were performed to test the affect of zeroing the devices. The KVH
gyro was attached to the cage to measure pitch and the cage was placed on a
table. Both devices were powered up
until their temperature
stabilized. Then, they were reset and their data was logged for approximately
one minute for the first test.
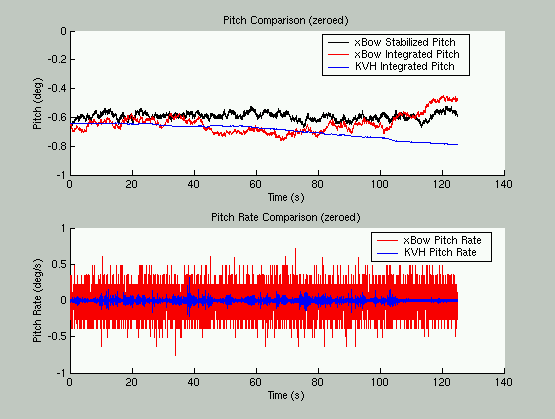
For the second test, the devices were zeroed. For the Crossbow, this involved sending
the command z200 which zeros the device over 2000 samples (approx 20 sec). The
KVH gyro does not have this capability, so the logging interface averages the
the reported rate over 20sec and then subtracts this bias from the raw
measurements.
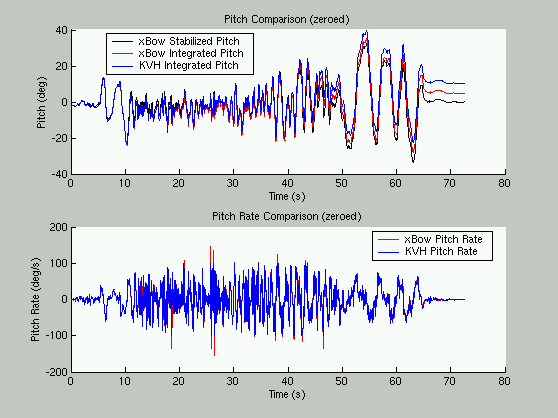
The results are presented below: