Figure 6: The introduction of uncertainty into a plan

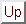

Uncertainty is introduced into a plan when an open condition in the
plan is achieved by an uncertain effect, i.e., an effect with an
unknown precondition. In the bomb-in-the-toilet example, for
instance, Cassandra may achieve the condition bomb is disarmed by
selecting the dunk operator, which has the preconditions
the package is at the toilet, and the bomb is in the
package. The condition the bomb is in the package can be
established by identifying it with the bomb is in package1,
which is an effect of the start operator. However, this
condition is uncertain, as can be determined by noting that it has an
unknown precondition. Cassandra will attempt to deal with this
uncertainty by introducing a new contingency (or new contingencies)
into the plan. The state of the plan just after the introduction of
the uncertainty is illustrated in Figure 6.

Figure 6: The introduction of uncertainty into a
plan